Online courses directory (237)
En temelinden en zorlarına kadar 2. derece denklemlerle ilgili herşeyi öğreneceksiniz.
2. Dereceden Eşitsizliklerle ilgili bilmeniz gereken her şeyi bu derste bulacaksınız.
The ACT (American College Testing) is a standardized test for high school achievement and college admissions in the United States produced by ACT, Inc. The ACT test has historically consisted of four tests: English, Mathematics, Reading, and Science Reasoning. The 60-question math test consists of 14 questions covering pre-algebra, 10 elementary algebra, 9 intermediate algebra, 14 plane geometry, 9 coordinate geometry, and 4 elementary trigonometry. This free online course from ALISON contains 60 sample problems similar to the ones you will find in your own. This course is ideal for any learner studying for the ACT math exam.<br />
<p>This course is ideal for people who want to gain a thorough understanding and knowledge of advanced topics in algebra. </p><br /> <p>The advanced algebra topics include linear equations, inequalities, graphs, matrices, polynomials, radical expressions, quadratic equations, functions, exponential, logarithmic expressions, sequences, series, probability and trigonometry. </p> <br /> <p>The course is divided into 13 modules and each module is divided into lessons with theory, examples and video explanations, making for an enhanced study experience. </p>
This free online training explores complex numbers and equations, polynomial equations, conics, advanced trigonometry, differentiation, antiderivatives, and vectors in 2- and 3-space. This course is both an ideal study-aid for students to improve their skills in their spare time or for anyone interested in exploring the world of mathematics.
The Advanced Mathematics Upper-Secondary 2 course completes our suit of upper-secondary maths. This free online course covers differential equations, kinematics, vector calculus and dynamics. This course is suitable for maths students, and for anyone interested in exploring the world of mathematics. <br /><br />
This free online course in algebra from ALISON will guide you through among other things expressions, systems of equations, functions, real numbers, inequalities, exponents, polynomials, radical and rational expressions. The course is divided into 12 chapters and each chapter is divided into several lessons. Under each lesson you will find theory, examples and video lessons. This course is ideal for learners who want to study topics in algebra in detail.
Build your earth science vocabulary and learn about cycles of matter and types of sedimentary rocks through the Education Portal course Earth Science 101: Earth Science. Our series of video lessons and accompanying self-assessment quizzes can help you boost your scientific knowledge ahead of the Excelsior Earth Science exam . This course was designed by experienced educators and examines both science basics, like experimental design and systems of measurement, and more advanced topics, such as analysis of rock deformation and theories of continental drift.
Build your earth science vocabulary and learn about cycles of matter and types of sedimentary rocks through the Education Portal course Earth Science 101: Earth Science. Our series of video lessons and accompanying self-assessment quizzes can help you boost your scientific knowledge ahead of the Excelsior Earth Science exam . This course was designed by experienced educators and examines both science basics, like experimental design and systems of measurement, and more advanced topics, such as analysis of rock deformation and theories of continental drift.
This free online course offers a comprehensive introduction to algebra and carefully explains the concepts of algebraic fractions. It guides you from basic operations, such as addition and subtraction, up to simplifying quadratic equations and more. It applies maths to real-world problems. This course is ideal for students looking for extra help, or even for a different approach to learning maths.
Algebra+ is a 10-week online course designed for students who have successfully completed high school algebra but who placed into pre-college level mathematics at their local college or university. This course is for refreshing their math skills with a review of pre-college level algebra. After successfully completing this course, the goal would be to retake your college
Understanding absolute value and solving absolute value equations and inequalities. Absolute Value and Number Lines. Absolute Value 1. Absolute Value of Integers. Comparing Absolute Values. CA Algebra I: Number Properties and Absolute Value. Absolute Value Equations. Absolute Value Equations Example 1. Absolute Value Equation Example 2. U02_L2_T2_we1 Absolute Value Equations.avi. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Inequalities 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3.
Select problems from ck12.org's Algebra 1 FlexBook (Open Source Textbook). This is a good playlist to review if you want to make sure you have a good understanding of all of the major topics in Algebra I. Variable Expressions. Order of Operations Example. Patterns and Equations. Equations and Inequalities. Domain and Range of a Function. Functions as Graphs. Word Problem Solving Plan 1. Word Problem Solving Strategies. Integers and Rational Numbers. Addition of Rational Numbers. Subtraction of Rational Numbers. Multiplication of Rational Numbers. Distributive Property Example 1. Division of Rational Numbers. Square Roots and Real Numbers. Problem Solving Word Problems 2. One Step Equations. Two-Step Equations. Ex 1: Distributive property to simplify . Ex 3: Distributive property to simplify . Ratio and Proportion. Scale and Indirect Measurement. Percent Problems. Another percent example. The Coordinate Plane. Graphing Using Intercepts. Graphs of Linear Equations. Slope and Rate of Change. Graphs Using Slope-Intercept Form. Direct Variation Models. Function example problems. Word Problem Solving 4. Linear Equations in Slope Intercept Form. Linear Equations in Point Slope Form. Linear Equations in Standard Form. Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Fitting a Line to Data. Predicting with Linear Models. Using a Linear Model. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. Compound Inequalities. Absolute Value Equations. Absolute Value Inequalities. Graphing Inequalities. Solving Linear Systems by Graphing. Solving Linear Systems by Substitution. Solving Systems of Equations by Elimination. Solving Systems of Equations by Multiplication. Special Types of Linear Systems. Systems of Linear Inequalities. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Exponent Properties Involving Quotients. Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents. Scientific Notation. Exponential Growth Functions. Exponential Decay Functions. Geometric Sequences (Introduction). Word Problem Solving- Exponential Growth and Decay. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials. Multiplication of Polynomials. Special Products of Binomials. Polynomial Equations in Factored Form. Factoring quadratic expressions. Factoring Special Products. Factor by Grouping and Factoring Completely. Graphs of Quadratic Functions. Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing. Solving Quadratic Equations by Square Roots. Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square. How to Use the Quadratic Formula. Proof of Quadratic Formula. Discriminant of Quadratic Equations. Linear, Quadratic, and Exponential Models. Identifying Quadratic Models. Identifying Exponential Models. Quadratic Regression. Shifting functions. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. More Simplifying Radical Expressions. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Radical Equation Examples. More Involved Radical Equation Example. Pythagorean Theorem. Distance Formula. Midpoint Formula. Visual Pythagorean Theorem Proof. Average or Central Tendency: Arithmetic Mean, Median, and Mode. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Stem and Leaf Plots. Histograms. Box-and-whisker Plot. Proportionality. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Polynomial Division. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions. Adding Rational Expressions Example 1. Adding Rational Expressions Example 2. Adding Rational Expressions Example 3. Solving Rational Equations. Two more examples of solving rational equations. Surveys and Samples.
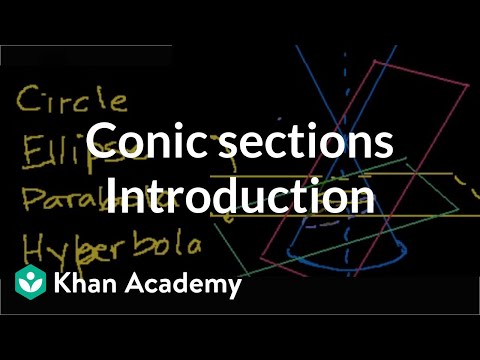
Identifying and graphing circles, ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in factored form. Completing the square to write equation in standard form of a circle. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Shifting and scaling parabolas. Parabola intuition example 1. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in factored form. Completing the square to write equation in standard form of a circle. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Shifting and scaling parabolas. Parabola intuition example 1. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples.
Solving exponential and radical expressions and equations. Using scientific notation and significant figures. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations.
Solving exponential and radical expressions and equations. Using scientific notation and significant figures. Understanding Exponents. Understanding Exponents 2. Exponent Rules 1. Exponent Rules 2. Level 1 Exponents. Level 2 Exponents. Negative Exponent Intuition. Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents. Level 3 exponents. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Negative and Positive Exponents. Exponent Properties Involving Quotients. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Pythagorean Theorem 1. Pythagorean Theorem 2. Pythagorean Theorem 3. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 2. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Scientific notation 1. Scientific notation 2. Scientific notation 3. Scientific Notation I. Scientific Notation Example 2. Scientific Notation 3 (new). Scientific Notation Examples. Multiplying in Scientific Notation. Significant Figures. More on Significant Figures. Addition and Subtraction with Significant Figures. Multiplying and Dividing with Significant Figures. Understanding Square Roots. Approximating Square Roots. Square Roots and Real Numbers. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Finding Cube Roots. Simplifying Cube Roots. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Simplifying radicals. Simplifying Radical Expressions1. Simplifying Radical Expressions 2. Simplifying Radical Expressions 3. More Simplifying Radical Expressions. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3.
Identifying, solving, and graphing various types of functions. What is a function. Difference between Equations and Functions. Function example problems. Ex: Constructing a function. Understanding Function Notation Example 1). Understanding Function Notation Example 2). Understanding Function Notation Example 3). Understanding function notation. Testing if a relationship is a function. Graphical Relations and Functions. Functions as Graphs. Recognizing functions (example 1). Recognizing functions (example 2). Recognizing functions. Relations and Functions. Functional Relationships 1. Recognizing functions (example 3). Recognizing functions (example 4). Recognizing functions (example 5). Recognizing functions 2. Domain of a function. Domain and Range of a Relation. Domain and Range of a Function Given a Formula. Domain and Range 1. Domain of a Radical Function. Domain of a function. Domain and Range 2. Domain and Range of a Function. Range of a function. Domain and range from graphs. Domain and range from graph. Direct and Inverse Variation. Recognizing Direct and Inverse Variation. Proportionality Constant for Direct Variation. Direct and inverse variation. Direct Variation Models. Direct Variation 1. Inverse Variation Application. Direct Inverse and Joint Variation. Direct Variation Application. Ex 1: Evaluating a function. Ex 2: Graphing a basic function. Graphing a parabola with a table of values. Ex 4: Graphing radical functions. Ex: Graphing exponential functions. Views of a function. Interpreting a graph exercise example. Interpreting graphs of linear and nonlinear functions. Quotient of Functions. Sum of Functions. Product of Functions. Difference of Functions. Evaluating a function expression. Evaluating expressions with function notation. Evaluating composite functions example. Evaluating composite functions. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Inverses of functions. New operator definitions. New operator definitions 1. New operator definitions 2. New operator definitions 2. Introduction to functions. Functions Part 2. Functions (Part III). Functions (part 4). What is a function. Difference between Equations and Functions. Function example problems. Ex: Constructing a function. Understanding Function Notation Example 1). Understanding Function Notation Example 2). Understanding Function Notation Example 3). Understanding function notation. Testing if a relationship is a function. Graphical Relations and Functions. Functions as Graphs. Recognizing functions (example 1). Recognizing functions (example 2). Recognizing functions. Relations and Functions. Functional Relationships 1. Recognizing functions (example 3). Recognizing functions (example 4). Recognizing functions (example 5). Recognizing functions 2. Domain of a function. Domain and Range of a Relation. Domain and Range of a Function Given a Formula. Domain and Range 1. Domain of a Radical Function. Domain of a function. Domain and Range 2. Domain and Range of a Function. Range of a function. Domain and range from graphs. Domain and range from graph. Direct and Inverse Variation. Recognizing Direct and Inverse Variation. Proportionality Constant for Direct Variation. Direct and inverse variation. Direct Variation Models. Direct Variation 1. Inverse Variation Application. Direct Inverse and Joint Variation. Direct Variation Application. Ex 1: Evaluating a function. Ex 2: Graphing a basic function. Graphing a parabola with a table of values. Ex 4: Graphing radical functions. Ex: Graphing exponential functions. Views of a function. Interpreting a graph exercise example. Interpreting graphs of linear and nonlinear functions. Quotient of Functions. Sum of Functions. Product of Functions. Difference of Functions. Evaluating a function expression. Evaluating expressions with function notation. Evaluating composite functions example. Evaluating composite functions. Introduction to Function Inverses. Function Inverse Example 1. Function Inverses Example 2. Function Inverses Example 3. Inverses of functions. New operator definitions. New operator definitions 1. New operator definitions 2. New operator definitions 2. Introduction to functions. Functions Part 2. Functions (Part III). Functions (part 4).
Use the power of algebra to understand and interpret points and lines (something we typically do in geometry). This will include slope and the equation of a line. Descartes and Cartesian Coordinates. The Coordinate Plane. Plot ordered pairs. Graphing points exercise. Graphing points. Quadrants of Coordinate Plane. Graphing points and naming quadrants exercise. Graphing points and naming quadrants. Points on the coordinate plane. Points on the coordinate plane. Coordinate plane word problems exercise. Coordinate plane word problems. Reflecting points exercise. Reflecting points. Ordered pair solutions of equations. Ordered Pair Solutions of Equations 2. Determining a linear equation by trying out values from a table. Equations from tables. Plotting (x,y) relationships. Graphs of Linear Equations. Application problem with graph. Ordered pair solutions to linear equations. Interpreting Linear Graphs. Exploring linear relationships. Recognizing Linear Functions. Interpreting linear relationships. Graphing lines 1. Recognizing Linear Functions. Linear and nonlinear functions (example 1). Linear and nonlinear functions (example 2). Linear and nonlinear functions (example 3). Linear and nonlinear functions. Graphing using X and Y intercepts. Graphing Using Intercepts. X and Y intercepts. X and Y intercepts 2. Solving for the x-intercept. Finding x intercept of a line. Finding intercepts for a linear function from a table. Linear function intercepts. Interpreting intercepts of linear functions. Interpreting and finding intercepts of linear functions. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex1. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex2. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex3. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships. Comparing proportional relationships. Constructing an equation for a proportional relationship. Constructing and comparing proportional relationships. Graphing proportional relationships example. Graphing proportional relationships example 2. Graphing proportional relationships example 3. Graphing proportional relationships. Comparing rates. Representing and comparing rates. Rates and proportional relationships. Rate problem with fractions 1. Unit cost with fractions 1. Rate problems 1. Slope of a line. Slope of a Line 2. Slope and Rate of Change. Graphical Slope of a Line. Slope of a Line 3. Slope Example. Hairier Slope of Line. Identifying slope of a line. Slope and Y-intercept Intuition. Line graph intuition. Algebra: Slope. Algebra: Slope 2. Algebra: Slope 3. Graphing a line in slope intercept form. Converting to slope-intercept form. Graphing linear equations. Fitting a Line to Data. Comparing linear functions 1. Comparing linear functions 2. Comparing linear functions 3. Comparing linear functions. Interpreting features of linear functions example. Interpreting features of linear functions example 2. Interpreting features of linear functions. Comparing linear functions applications 1. Comparing linear functions applications 2. Comparing linear functions applications 3. Comparing linear functions applications. Constructing a linear function word problem. Constructing and interpreting a linear function. Constructing linear graphs. Constructing and interpreting linear functions. Multiple examples of constructing linear equations in slope-intercept form. Constructing equations in slope-intercept form from graphs. Constructing linear equations to solve word problems. Linear equation from slope and a point. Finding a linear equation given a point and slope. Equation of a line from fractional slope and point. Constructing the equation of a line given two points. Finding y intercept given slope and point. Solving for the y-intercept. Slope intercept form from table. Slope intercept form. Idea behind point slope form. Linear Equations in Point Slope Form. Point slope form. Linear Equations in Standard Form. Point-slope and standard form. Converting between slope-intercept and standard form. Converting from point slope to slope intercept form. Converting between point-slope and slope-intercept. Finding the equation of a line. Midpoint formula. Midpoint formula. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean theorem. Distance Formula. Distance formula. Perpendicular Line Slope. Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Parallel Line Equation. Parallel Lines. Parallel Lines 2. Parallel lines 3. Perpendicular Lines. Perpendicular lines 2. Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines. Distance between a point and a line. Distance between point and line. Algebra: Slope and Y-intercept intuition. Algebra: Equation of a line. CA Algebra I: Slope and Y-intercept. Graphing Inequalities. Solving and graphing linear inequalities in two variables 1. Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Example 2. Graphing Inequalities 2. Graphing linear inequalities in two variables 3. Graphs of inequalities. Graphing linear inequalities. Graphing Inequalities 1. Graphing and solving linear inequalities. CA Algebra I: Graphing Inequalities. Similar triangles to prove that the slope is constant for a line. Slope and triangle similarity 1. Slope and triangle similarity 2. Slope and triangle similarity 3. Slope and triangle similarity 4. Slope and triangle similarity. Average Rate of Change Example 1). Average Rate of Change Example 2). Average Rate of Change Example 3). Average rate of change when function defined by equation. Average rate of change. Descartes and Cartesian Coordinates. The Coordinate Plane. Plot ordered pairs. Graphing points exercise. Graphing points. Quadrants of Coordinate Plane. Graphing points and naming quadrants exercise. Graphing points and naming quadrants. Points on the coordinate plane. Points on the coordinate plane. Coordinate plane word problems exercise. Coordinate plane word problems. Reflecting points exercise. Reflecting points. Ordered pair solutions of equations. Ordered Pair Solutions of Equations 2. Determining a linear equation by trying out values from a table. Equations from tables. Plotting (x,y) relationships. Graphs of Linear Equations. Application problem with graph. Ordered pair solutions to linear equations. Interpreting Linear Graphs. Exploring linear relationships. Recognizing Linear Functions. Interpreting linear relationships. Graphing lines 1. Recognizing Linear Functions. Linear and nonlinear functions (example 1). Linear and nonlinear functions (example 2). Linear and nonlinear functions (example 3). Linear and nonlinear functions. Graphing using X and Y intercepts. Graphing Using Intercepts. X and Y intercepts. X and Y intercepts 2. Solving for the x-intercept. Finding x intercept of a line. Finding intercepts for a linear function from a table. Linear function intercepts. Interpreting intercepts of linear functions. Interpreting and finding intercepts of linear functions. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex1. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex2. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships ex3. Analyzing and identifying proportional relationships. Comparing proportional relationships. Constructing an equation for a proportional relationship. Constructing and comparing proportional relationships. Graphing proportional relationships example. Graphing proportional relationships example 2. Graphing proportional relationships example 3. Graphing proportional relationships. Comparing rates. Representing and comparing rates. Rates and proportional relationships. Rate problem with fractions 1. Unit cost with fractions 1. Rate problems 1. Slope of a line. Slope of a Line 2. Slope and Rate of Change. Graphical Slope of a Line. Slope of a Line 3. Slope Example. Hairier Slope of Line. Identifying slope of a line. Slope and Y-intercept Intuition. Line graph intuition. Algebra: Slope. Algebra: Slope 2. Algebra: Slope 3. Graphing a line in slope intercept form. Converting to slope-intercept form. Graphing linear equations. Fitting a Line to Data. Comparing linear functions 1. Comparing linear functions 2. Comparing linear functions 3. Comparing linear functions. Interpreting features of linear functions example. Interpreting features of linear functions example 2. Interpreting features of linear functions. Comparing linear functions applications 1. Comparing linear functions applications 2. Comparing linear functions applications 3. Comparing linear functions applications. Constructing a linear function word problem. Constructing and interpreting a linear function. Constructing linear graphs. Constructing and interpreting linear functions. Multiple examples of constructing linear equations in slope-intercept form. Constructing equations in slope-intercept form from graphs. Constructing linear equations to solve word problems. Linear equation from slope and a point. Finding a linear equation given a point and slope. Equation of a line from fractional slope and point. Constructing the equation of a line given two points. Finding y intercept given slope and point. Solving for the y-intercept. Slope intercept form from table. Slope intercept form. Idea behind point slope form. Linear Equations in Point Slope Form. Point slope form. Linear Equations in Standard Form. Point-slope and standard form. Converting between slope-intercept and standard form. Converting from point slope to slope intercept form. Converting between point-slope and slope-intercept. Finding the equation of a line. Midpoint formula. Midpoint formula. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean theorem. Distance Formula. Distance formula. Perpendicular Line Slope. Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Parallel Line Equation. Parallel Lines. Parallel Lines 2. Parallel lines 3. Perpendicular Lines. Perpendicular lines 2. Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines. Distance between a point and a line. Distance between point and line. Algebra: Slope and Y-intercept intuition. Algebra: Equation of a line. CA Algebra I: Slope and Y-intercept. Graphing Inequalities. Solving and graphing linear inequalities in two variables 1. Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables Example 2. Graphing Inequalities 2. Graphing linear inequalities in two variables 3. Graphs of inequalities. Graphing linear inequalities. Graphing Inequalities 1. Graphing and solving linear inequalities. CA Algebra I: Graphing Inequalities. Similar triangles to prove that the slope is constant for a line. Slope and triangle similarity 1. Slope and triangle similarity 2. Slope and triangle similarity 3. Slope and triangle similarity 4. Slope and triangle similarity. Average Rate of Change Example 1). Average Rate of Change Example 2). Average Rate of Change Example 3). Average rate of change when function defined by equation. Average rate of change.
Understanding and solving equations with imaginary numbers. Introduction to i and Imaginary Numbers. Calculating i Raised to Arbitrary Exponents. Imaginary unit powers. Imaginary Roots of Negative Numbers. i as the Principal Root of -1 (a little technical). Complex numbers. Complex numbers (part 1). Complex numbers (part 2). Plotting complex numbers on the complex plane. The complex plane. Adding Complex Numbers. Subtracting Complex Numbers. Adding and subtracting complex numbers. Multiplying Complex Numbers. Multiplying complex numbers. Complex Conjugates Example. Dividing Complex Numbers. Dividing complex numbers. Absolute value of a complex number. Absolute value of complex numbers. Example: Complex roots for a quadratic. Algebra II: Imaginary and Complex Numbers. Introduction to i and Imaginary Numbers. Calculating i Raised to Arbitrary Exponents. Imaginary unit powers. Imaginary Roots of Negative Numbers. i as the Principal Root of -1 (a little technical). Complex numbers. Complex numbers (part 1). Complex numbers (part 2). Plotting complex numbers on the complex plane. The complex plane. Adding Complex Numbers. Subtracting Complex Numbers. Adding and subtracting complex numbers. Multiplying Complex Numbers. Multiplying complex numbers. Complex Conjugates Example. Dividing Complex Numbers. Dividing complex numbers. Absolute value of a complex number. Absolute value of complex numbers. Example: Complex roots for a quadratic. Algebra II: Imaginary and Complex Numbers.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.