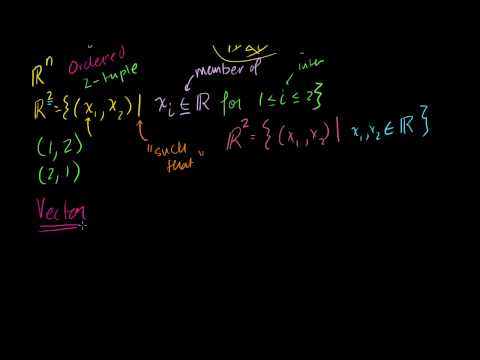Online courses directory (381)
Not all things with four sides have to be squares or rectangles! We will now broaden our understanding of quadrilaterals!. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Whether a Special Quadrilateral Can Exist. Rhombus Diagonals. Quadrilateral Overview. Quadrilateral Properties. Proof - Opposite Sides of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Diagonals of a Parallelogram Bisect Each Other. Proof - Opposite Angles of Parallelogram Congruent. Proof - Rhombus Diagonals are Perpendicular Bisectors. Proof - Rhombus Area Half Product of Diagonal Length. Area of a Parallelogram. Whether a Special Quadrilateral Can Exist. Rhombus Diagonals.
Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used). Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used).
This topic introduces the basic conceptual tools that underpin our journey through Euclidean geometry. These include the ideas of points, lines, line segments, rays, and planes. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment.
Thermo Can.
Brushed DC motor explained. Build your own motor. Compare the hair dryer motor to the one you can build.
Videos exploring the way things work. What is inside an alarm clock radio?. What is inside a coffee maker?. What is inside a tap light?. What is inside a hair dryer? (1 of 2). What is inside a hair dryer? (2 of 2). Compare the hair dryer motor to the one you can build. What is inside a DVD player? (1 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (2 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (3 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (4 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (5 of 5). What is inside a universal remote control?. What is inside a digital camera? (1 of 2). What is inside a digital camera? (2 of 2). What is inside an alarm clock radio?. What is inside a coffee maker?. What is inside a tap light?. What is inside a hair dryer? (1 of 2). What is inside a hair dryer? (2 of 2). Compare the hair dryer motor to the one you can build. What is inside a DVD player? (1 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (2 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (3 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (4 of 5). What is inside a DVD player? (5 of 5). What is inside a universal remote control?. What is inside a digital camera? (1 of 2). What is inside a digital camera? (2 of 2).
1 Spout Introduction. 2 Attach Spout's lever switches and motors. 3 Attach Spout's wires and connectors. 4 Attach Spout's sliding switches and resistors. 5 Connect Spout's antenna. 6 Attach Spout's LED eyes. 7 See inside Spout's motors and switches.
1. Bit-zee. 2. Bit-zee (long version). 3. Bit-zee Bot Introduction. 4. Bit-zee planning and propulsion. 5. Bit-zee's bits. 6. Bit-zee's chassis/frame. 7. Bit-zee's wheel mounts and fenders. 8. Bit-zee's component mounting holes. 9. Bit-zee's batteries. 10. Improving the battery wires. 11. Connecting Bit-zee's power wires and on-off switch. 12. Bit-zee's motors. 13. Why does Bit-zee need a motor controller?. 14. Bit-zee's motor controller. 15. Attaching and wiring Bit-zee's motor controller. 16. Attaching Bit-zee's Arduino. 17. How to hotwire a digital camera. 18. Attaching Bit-zee's digital camera. 19. Bit zee's 5 Volt power distribution board. 20. Hacking and attaching a digital recorder/player to Bit-zee. 21. Making a power connector for the Arduino. 22. Attaching Bit-zee's prototype board. 23. Connecting the motor controller to the Arduino. 24. Connecting Bit-zee's camera to the Arduino. 25. Bit-zee's bumper switches. 26. Bit-zee's eyes. 27. Bit-zee's IR sensor. 28. Bit-zee's shell. 29. Camera wiring update.
How have humans protected their secret messages through history? What has changed today?. What is Cryptography?. Probability Space. The Caesar Cipher. Caesar Cipher Exploration. Frequency Fingerprint Exploration . Polyalphabetic Cipher. Polyalphabetic Exploration. The One-Time Pad. Perfect Secrecy Exploration. Frequency Stability. Coin flip sequences. Frequency Stability Exploration. The Enigma Encryption Machine (case study). Perfect Secrecy. Pseudorandom Number Generators. Random Walk Exploration. Ciphers vs. Codes. Shift Cipher. Caesar cipher encryption. Caesar Cipher Decryption. Caesar cipher frequency analysis. Vigenere cipher encryption. XOR Bitwise Operation. XOR & the One-Time Pad. XOR Exploration. Bitwise Operators. What's Next?. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Public Key Cryptography: what is it?. The Discrete Logarithm Problem. Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange. RSA Encryption: step 1. RSA Encryption: step 2. RSA Encryption: step 3. Time Complexity (Exploration). Euler's Totient Function. Euler Totient Exploration. RSA Encryption: step 4. What should we learn next?. What is Modular Arithmetic?. Modulo Operator. Congruence Modulo. Congruence Relation. Equivalence Relations. The Quotient Remainder Theorem. Modular Addition & Subtraction. Modular Addition. Modular Multiplication. Modular Multiplication. Modular Exponentiation. Fast Modular Exponentiation. Fast Modular Exponentiation. Modular Inverses. Introduction. Primality Test Challenge. Trial Division. Level 1: Primality Test. Running Time. Level 2: measuring running time. Computer Memory (space). Binary Memory Exploration. Algorithmic Efficiency. Level 3: Challenge. Sieve of Eratosthenes. Level 4: Sieve of Eratosthenes. Primality Test with Sieve. Level 5: Trial division using sieve. The Prime Number Theorem. Prime density spiral. Prime Gaps. Time Space Tradeoff. Summary (what's next?). Randomized Algorithms (intro). Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Guess the coin. Random Primality Test (warm up). Level 9: Trial Divison vs Random Division. Fermat's Little Theorem. Fermat Primality Test. Level 10: Fermat Primality Test. What's Next?. What is Cryptography?. Probability Space. The Caesar Cipher. Caesar Cipher Exploration. Frequency Fingerprint Exploration . Polyalphabetic Cipher. Polyalphabetic Exploration. The One-Time Pad. Perfect Secrecy Exploration. Frequency Stability. Coin flip sequences. Frequency Stability Exploration. The Enigma Encryption Machine (case study). Perfect Secrecy. Pseudorandom Number Generators. Random Walk Exploration. Ciphers vs. Codes. Shift Cipher. Caesar cipher encryption. Caesar Cipher Decryption. Caesar cipher frequency analysis. Vigenere cipher encryption. XOR Bitwise Operation. XOR & the One-Time Pad. XOR Exploration. Bitwise Operators. What's Next?. The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Public Key Cryptography: what is it?. The Discrete Logarithm Problem. Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange. RSA Encryption: step 1. RSA Encryption: step 2. RSA Encryption: step 3. Time Complexity (Exploration). Euler's Totient Function. Euler Totient Exploration. RSA Encryption: step 4. What should we learn next?. What is Modular Arithmetic?. Modulo Operator. Congruence Modulo. Congruence Relation. Equivalence Relations. The Quotient Remainder Theorem. Modular Addition & Subtraction. Modular Addition. Modular Multiplication. Modular Multiplication. Modular Exponentiation. Fast Modular Exponentiation. Fast Modular Exponentiation. Modular Inverses. Introduction. Primality Test Challenge. Trial Division. Level 1: Primality Test. Running Time. Level 2: measuring running time. Computer Memory (space). Binary Memory Exploration. Algorithmic Efficiency. Level 3: Challenge. Sieve of Eratosthenes. Level 4: Sieve of Eratosthenes. Primality Test with Sieve. Level 5: Trial division using sieve. The Prime Number Theorem. Prime density spiral. Prime Gaps. Time Space Tradeoff. Summary (what's next?). Randomized Algorithms (intro). Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Guess the coin. Random Primality Test (warm up). Level 9: Trial Divison vs Random Division. Fermat's Little Theorem. Fermat Primality Test. Level 10: Fermat Primality Test. What's Next?.
We've always been communicating.... as we moved from signal fires, to alphabets & electricity the problems remained the same. What is Information Theory?. Prehistory: Proto-writing. Ptolemaic: Rosetta Stone. Ancient History: The Alphabet. Source Encoding. Visual Telegraphs (case study). Decision Tree Exploration. Electrostatic Telegraphs (case study). The Battery & Electromagnetism. Morse Code & The Information Age. Morse code Exploration. What's Next?. Symbol Rate. Symbol Rate Exploration. Introduction to Channel Capacity. Message Space Exploration. Measuring Information. Galton Board Exploration. Origin of Markov Chains. Markov Chain Exploration. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Markov Text Exploration. What's Next?. What is Information Theory?. Prehistory: Proto-writing. Ptolemaic: Rosetta Stone. Ancient History: The Alphabet. Source Encoding. Visual Telegraphs (case study). Decision Tree Exploration. Electrostatic Telegraphs (case study). The Battery & Electromagnetism. Morse Code & The Information Age. Morse code Exploration. What's Next?. Symbol Rate. Symbol Rate Exploration. Introduction to Channel Capacity. Message Space Exploration. Measuring Information. Galton Board Exploration. Origin of Markov Chains. Markov Chain Exploration. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Markov Text Exploration. What's Next?.
Watch fun, educational videos on all sorts of Physics questions. Bridge Design and Destruction! (part 1). Bridge Design (and Destruction!) Part 2. Shifts in Equilibrium. The Marangoni Effect: How to make a soap propelled boat!. The Invention of the Battery. The Forces on an Airplane. Bouncing Droplets: Superhydrophobic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces. A Crash Course on Indoor Flying Robots.
What makes living things tick?. Homeostasis. A Voyage to Mars: Bone Loss in Space. Bread Mold Kills Bacteria.
Watch fun, educational videos on all sorts of Materials, how they're created and what they can do. Flocculation: Making Clean Water.
Everything in the universe can be measured. Earth's Tilt 1: The Reason for the Seasons. Earth's Tilt 2: Land of the Midnight Sun. 2D Equilibrium -- Balancing Games.
18. Attaching Bit-zee's digital camera.
Reenact the discovery of electromagnetism. The Magic of Discovery. Discovery of Magnetism. Discovery of Magnetic Fields. Electromagnet.
What is Programming?. Sneak Peek: Making An Awesome Program. A Tour of Programming on Khan Academy.
Fractional reserve banking and the money supply. Overview of Fractional Reserve Banking. Weaknesses of Fractional Reserve Lending. Full Reserve Banking. Money Supply- M0 M1 and M2. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting part 1. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting (part 2). Interest as Rent for Money. Money Supply and Demand Impacting Interest Rates. Overview of Fractional Reserve Banking. Weaknesses of Fractional Reserve Lending. Full Reserve Banking. Money Supply- M0 M1 and M2. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting part 1. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting (part 2). Interest as Rent for Money. Money Supply and Demand Impacting Interest Rates.
Let's get our feet wet by thinking in terms of vectors and spaces. Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Scaling vectors. Adding vectors. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A). Introduction to Vectors. Vector Examples. Scaling vectors. Adding vectors. Parametric Representations of Lines. Linear Combinations and Span. Introduction to Linear Independence. More on linear independence. Span and Linear Independence Example. Linear Subspaces. Basis of a Subspace. Vector Dot Product and Vector Length. Proving Vector Dot Product Properties. Proof of the Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Vector Triangle Inequality. Defining the angle between vectors. Defining a plane in R3 with a point and normal vector. Cross Product Introduction. Proof: Relationship between cross product and sin of angle. Dot and Cross Product Comparison/Intuition. Vector Triple Product Expansion (very optional). Normal vector from plane equation. Point distance to plane. Distance Between Planes. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 1. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 2. Matrices: Reduced Row Echelon Form 3. Matrix Vector Products. Introduction to the Null Space of a Matrix. Null Space 2: Calculating the null space of a matrix. Null Space 3: Relation to Linear Independence. Column Space of a Matrix. Null Space and Column Space Basis. Visualizing a Column Space as a Plane in R3. Proof: Any subspace basis has same number of elements. Dimension of the Null Space or Nullity. Dimension of the Column Space or Rank. Showing relation between basis cols and pivot cols. Showing that the candidate basis does span C(A).
Understanding how we can map one set of vectors to another set. Matrices used to define linear transformations. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.