Online courses directory (19947)
Quantum computation is a remarkable subject building on the great computational discovery that computers based on quantum mechanics are exponentially powerful. This course aims to make this cutting-edge material broadly accessible to undergraduate students, including computer science majors who do not have any prior exposure to quantum mechanics. The course starts with a simple introduction to the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics using the concepts of qubits (or quantum bits) and quantum gates. This treatment emphasizes the paradoxical nature of the subject, including entanglement, non-local correlations, the no-cloning theorem and quantum teleportation. The course covers the fundamentals of quantum algorithms, including the quantum fourier transform, period finding, Shor's quantum algorithm for factoring integers, as well as the prospects for quantum algorithms for NP-complete problems. It also discusses the basic ideas behind the experimental realization of quantum computers, including the prospects for adiabatic quantum optimization and the D-Wave controversy.
Before your course starts, try the new edX Demo where you can explore the fun, interactive learning environment and virtual labs. Learn more.
Do I need a textbook for this class?
No. Notes will be posted each week. If you wish to consult other references, a list of related textbooks and online resources will be provided.
What is the estimated effort for course?
About 5-12 hrs/week.
Why is the work load range so wide?
How long you spend on the course depends upon your background and on the depth to which you wish to understand the material. The topics in this course are quite open ended, and will be presented so you can understand them at a high level or can try to follow it at a sophisticated level with the help of the posted notes.
How much does it cost to take the course?
Nothing! The course is free.
Will the text of the lectures be available?
Yes. All of our lectures will have transcripts synced to the videos.
Do I need to watch the lectures live?
No. You can watch the lectures at your leisure.
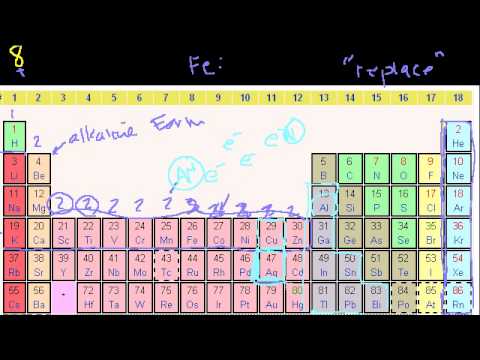
Groups of the Periodic Table. Valence Electrons. Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy. Other Periodic Table Trends. Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds. Groups of the Periodic Table. Valence Electrons. Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy. Other Periodic Table Trends. Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic Bonds.
Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used). Language and Notation of the Circle. Circles: Radius, Diameter and Circumference. Length of an arc that subtends a central angle. Finding central angle measure given arc length. Parts of a Circle. Area of a Circle. Area of a sector given a central angle. Inscribed and Central Angles. Perpendicular Radius Bisects Chord. Right Triangles Inscribed in Circles (Proof). Area of Inscribed Equilateral Triangle (some basic trig used).
Find out what's inside of blood. What's Inside of Blood?. Hemoglobin moves O2 and CO2. Bohr Effect vs. Haldane Effect. Fetal Hemoglobin and Hematocrit. Oxygen Content. What's Inside of Blood?. Hemoglobin moves O2 and CO2. Bohr Effect vs. Haldane Effect. Fetal Hemoglobin and Hematocrit. Oxygen Content.
Learn to defend and protect vital company information using the latest technology and defense strategies. Analyze internal and external threats to proactively prevent information attacks. Gain experience by solving real-world problems and leave the class equipped to establish and oversee information security.
This course is part of the MITx MicroMasters program in Data, Economics, and Development Policy (DEDP). To audit this course, click “Enroll Now” in the green button at the top of this page.
To enroll in the MicroMasters track or to learn more about this program and how it integrates with MIT’s new blended Master’s degree, go to MITx’s MicroMasters portal.
This is a course for those who are interested in the challenge posed by massive and persistent world poverty, and are hopeful that economists might have something useful to say about this challenge. The questions we will take up include: Is extreme poverty a thing of the past? What is economic life like when living under a dollar per day? Are the poor always hungry? How do we make schools work for poor citizens? How do we deal with the disease burden? Is microfinance invaluable or overrated? Without property rights, is life destined to be "nasty, brutish and short"? Should we leave economic development to the market? Should we leave economic development to non-governmental organizations (NGOs)? Does foreign aid help or hinder? Where is the best place to intervene? And many others.
At the end of this course, you should have a good sense of the key questions asked by scholars interested in poverty today, and hopefully a few answers as well.
This class will give you an introduction to the fundamentals of programming languages. Key concepts include how to specify and process valid strings, sentences and program structures.
Triangles are not always right (although they are never wrong), but when they are it opens up an exciting world of possibilities. Not only are right triangles cool in their own right (pun intended), they are the basis of very important ideas in analytic geometry (the distance between two points in space) and trigonometry. Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean Theorem 1. Pythagorean Theorem 2. Pythagorean Theorem 3. Pythagorean theorem. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem II. Garfield's proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. Bhaskara's proof of Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem Proof Using Similarity. Another Pythagorean Theorem Proof. 30-60-90 Triangle Side Ratios Proof. 45-45-90 Triangle Side Ratios. 30-60-90 Triangle Example Problem. Special right triangles. Area of a Regular Hexagon. 45-45-90 Triangles. Intro to 30-60-90 Triangles. 30-60-90 Triangles II. Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean theorem intro. Pythagorean Theorem 1. Pythagorean Theorem 2. Pythagorean Theorem 3. Pythagorean theorem. Introduction to the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem II. Garfield's proof of the Pythagorean Theorem. Bhaskara's proof of Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem Proof Using Similarity. Another Pythagorean Theorem Proof. 30-60-90 Triangle Side Ratios Proof. 45-45-90 Triangle Side Ratios. 30-60-90 Triangle Example Problem. Special right triangles. Area of a Regular Hexagon. 45-45-90 Triangles. Intro to 30-60-90 Triangles. 30-60-90 Triangles II.
Think about the oldest and most familiar principles of American law, property and proportional liability, in a new and surprising way, and learn to apply economic reasoning to an especially important and interesting aspect of life.
To acquire an understanding of the fundamental concepts of genomics and biotechnology, and their implications for human biology, evolution, medicine, social policy and individual life path choices in the 21st century.
Solving exponential and radical expressions and equations. Using scientific notation and significant figures. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations. Negative and Positive Exponents. Evaluating exponential expressions. Evaluating exponential expressions 3. Exponent Rules Part 1. Exponent Rules Part 2. Exponent Properties 1. Exponent Properties 2. Exponent Properties 3. Exponent Properties 4. Simplifying rational expression with exponent properties. Exponent Properties 5. Exponent Properties 6. Exponent Properties 7. Simplifying Square Roots. Simplifying Square Roots Comment Response. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents. Radical Equivalent to Rational Exponents 2. Radical Expressions with Higher Roots. Adding and Simplifying Radicals. Subtracting and Simplifying Radicals. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 1. Multiply and Simplify a Radical Expression 2. Exponent Properties Involving Products. Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. Simplifying Cube Roots. More Rational Exponents and Exponent Laws. How to Rationalize a Denominator. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 2. Simplifying Expressions with Exponents 3. Fractional Exponent Expressions 1. Fractional Exponent Expressions 2. Fractional Exponent Expressions 3. Simplifying expressions with exponents. Solving Radical Equations. Extraneous Solutions to Radical Equations. Solving Radical Equations 1. Solving Radical Equations 2. Solving Radical Equations 3. Applying Radical Equations 1. Applying Radical Equations 2. Applying Radical Equations 3. Radical equations.
Extending our understanding of numbers below 0. Thinking about "absolute" distance from 0. Negative Numbers Introduction. Negative numbers on the number line. Number line 3. Ordering Negative Numbers. Ordering negative numbers. Number opposites. Number opposites. Negative Numbers Introduction. Number opposites. Example: Adding negative numbers. Example: Adding integers with different signs. Adding negative numbers. Adding and subtracting negative number examples. Why Subtracting a Negative Equivalent to Adding a Positive. Adding and subtracting negative numbers. Negative number word problems 1. Negative number word problems. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Adding/Subtracting negative numbers. Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers. Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive. Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes Intuitive Sense. Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers. Example: Multiplying numbers with different signs. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Absolute Value and Number Lines. Absolute Value 1. Finding absolute values. Absolute Value of Integers. Comparing Absolute Values. Comparing absolute values. Absolute value word problems exercise. Absolute value word problems. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Negative Numbers Introduction. Negative numbers on the number line. Number line 3. Ordering Negative Numbers. Ordering negative numbers. Number opposites. Number opposites. Negative Numbers Introduction. Number opposites. Example: Adding negative numbers. Example: Adding integers with different signs. Adding negative numbers. Adding and subtracting negative number examples. Why Subtracting a Negative Equivalent to Adding a Positive. Adding and subtracting negative numbers. Negative number word problems 1. Negative number word problems. Adding decimals of different signs word problem. Adding/Subtracting negative numbers. Multiplying Positive and Negative Numbers. Why a Negative Times a Negative is a Positive. Why a Negative Times a Negative Makes Intuitive Sense. Dividing Positive and Negative Numbers. Example: Multiplying numbers with different signs. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Multiplying and dividing negative numbers. Absolute Value and Number Lines. Absolute Value 1. Finding absolute values. Absolute Value of Integers. Comparing Absolute Values. Comparing absolute values. Absolute value word problems exercise. Absolute value word problems. Constructing and interpreting absolute value. Constructing and interpreting absolute value.
Were the Middle Ages really all that dark? Hardly! How could we call the period that saw the building of Chartres Cathedral with its stunning stained-glass windows, dark? Sure, the Roman empire collapsed, but with the Christianization of Europe came magnificent churches, illuminated bibles, and intricately designed broaches. This period also saw the birth of Islam, the third great monotheistic religion. Introduction. Medieval and Byzantine Art. A New Pictorial Language: The Image in Early Medieval Art. Iconoclasm. Medieval Manuscripts. The Bestiary. Beginner's Guide to Medieval Art. An Introduction to Christianity. Standard Scenes from the Life of Christ in Art. An Introduction to Early Christian Art. Early Christian Art & Architecture after Constantine. Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus. Santa Sabina. Santa Maria Maggiore. The Mausoleum of Galla Placidia, Ravenna. Early Christian. Sutton Hoo Ship Burial. The Lindesfarne Gospels. Medieval and Byzantine Art. San Vitale. Sant'Apollinare in Classe, Ravenna, Italy, c. 533-49. Hagia Sophia. Ivory panel with Archangel. Icon of Saint George (the "Black George"). Icon of the Triumph of Orthodoxy. Byzantine Art. Introduction to Islam. The Five Pillars of Islam. Arts of the Islamic World. Two Royal Figures (Saljuq Period). Coronation Mantle. Ilkhanid Mihrab. Hebrew Astrolabe. Qa'a: The Damascus Room. Carolingian Art: An Introduction. Charlemagne: An Introduction (1 of 2). Charlemagne and the Carolingian Revival (part 2 of 2). Saint Matthew from the Ebbo Gospel. Lindau Gospels Cover. Santa Prassede (Praxedes). Carolingian. Ottonian Art: An Introduction. Bronze doors, Saint Michael's, Hildesheim, commissioned by Bishop Bernward, 1015. Pilgrimage Routes and the Cult of the Relic. Pentecost and Mission to the Apostles Tympanum, V
Exploring a world where both sides aren't equal anymore!. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1. Inequalities Using Multiplication and Division. One-step inequality with multiplication and division example. Constructing and solving one-step inequality. One step inequalities. One-Step inequality involving addition. Inequalities Using Addition and Subtraction. Two-step inequality example. Multi-Step Inequalities. Multi-Step Inequalities 2. Multi-Step Inequalities 3. Multi-step linear inequalities. Interpreting Inequalities. Writing and using inequalities 2. Writing and using inequalities 3. Interpreting and solving linear inequalities. Inequality examples. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities. Compound Inequalities 2. Compound Inequalities 3. Compound Inequalities 4. Compound inequalities. Absolute Value Inequalities. Absolute value inequalities Example 1. Absolute Value Inequalities Example 2. Absolute value inequalities example 3. Writing and using inequalities. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store visual argument. Dogs cats and bears in a pet store analytic argument. Reasoning through inequality expressions. Using expressions to understand relationships. Structure in expressions 1.
This topic introduces the basic conceptual tools that underpin our journey through Euclidean geometry. These include the ideas of points, lines, line segments, rays, and planes. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment. Euclid as the Father of Geometry. Language and Notation of Basic Geometry. Lines, Line Segments, and Rays. Recognizing rays lines and line segments. Specifying planes in three dimensions. Points, lines, and planes. Language and Notation of the Circle. The Golden Ratio. Identifying Rays. Measuring segments. Measuring segments. Congruent segments. Congruent segments. Segment addition. Segment addition. Algebraic midpoint of a segment exercise. Midpoint of a segment.
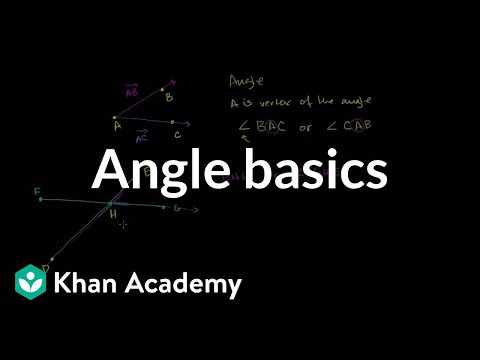
This topic continues our journey through the world of Euclid by helping us understand angles and how they can relate to each other. Angle basics. Measuring angles in degrees. Using a protractor. Measuring angles. Measuring angles. Acute right and obtuse angles. Angle types. Vertical, adjacent and linearly paired angles. Exploring angle pairs. Introduction to vertical angles. Vertical angles. Using algebra to find the measures of vertical angles. Vertical angles 2. Proof-Vertical Angles are Equal. Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals. Identifying Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Figuring out angles between transversal and parallel lines. Congruent angles. Parallel lines 1. Using algebra to find measures of angles formed from transversal. Parallel lines 2. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. Proof - Sum of Measures of Angles in a Triangle are 180. Triangle Angle Example 1. Triangle Angle Example 2. Triangle Angle Example 3. Challenging Triangle Angle Problem. Proof - Corresponding Angle Equivalence Implies Parallel Lines. Finding more angles. Angles 1. Angles 2. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Angles of a polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Introduction to angles (old). Angles (part 2). Angles (part 3). Angles formed between transversals and parallel lines. Angles of parallel lines 2. The Angle Game. Angle Game (part 2). Acute right and obtuse angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of complementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of supplementary angles. Angle addition postulate. Angle basics. Measuring angles in degrees. Using a protractor. Measuring angles. Measuring angles. Acute right and obtuse angles. Angle types. Vertical, adjacent and linearly paired angles. Exploring angle pairs. Introduction to vertical angles. Vertical angles. Using algebra to find the measures of vertical angles. Vertical angles 2. Proof-Vertical Angles are Equal. Angles Formed by Parallel Lines and Transversals. Identifying Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. Figuring out angles between transversal and parallel lines. Congruent angles. Parallel lines 1. Using algebra to find measures of angles formed from transversal. Parallel lines 2. CA Geometry: Deducing Angle Measures. Proof - Sum of Measures of Angles in a Triangle are 180. Triangle Angle Example 1. Triangle Angle Example 2. Triangle Angle Example 3. Challenging Triangle Angle Problem. Proof - Corresponding Angle Equivalence Implies Parallel Lines. Finding more angles. Angles 1. Angles 2. Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon. Angles of a polygon. Sum of the exterior angles of convex polygon. Introduction to angles (old). Angles (part 2). Angles (part 3). Angles formed between transversals and parallel lines. Angles of parallel lines 2. The Angle Game. Angle Game (part 2). Acute right and obtuse angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Complementary and supplementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of complementary angles. Example using algebra to find measure of supplementary angles. Angle addition postulate.
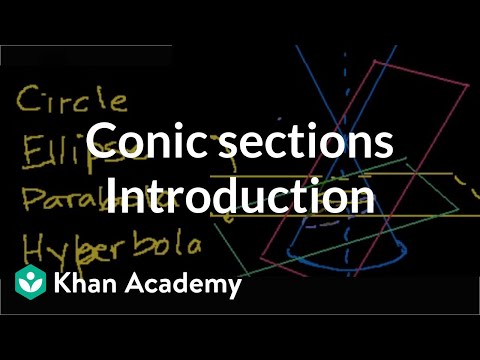
A detailed look at shapes that are prevalent in science: conic sections. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Radius and center for a circle equation in standard form. Equation of a circle in factored form. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples. Tangent Line Hyperbola Relationship (very optional). IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 1. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 2. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 3. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 4. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 5. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Intersection. Introduction to Conic Sections. Recognizing conic sections. Radius and center for a circle equation in standard form. Equation of a circle in factored form. Conic Sections: Intro to Circles. Graphing circles. Equation of a circle in non-factored form. Graphing circles 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Ellipses. Equation of an ellipse. Foci of an Ellipse. Parabola Focus and Directrix 1. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola 2. Parabola intuition 1. Parabola intuition 2. Conic Sections: Intro to Hyperbolas. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 2. Conic Sections: Hyperbolas 3. Equation of a hyperbola. Foci of a Hyperbola. Proof: Hyperbola Foci. Identifying an ellipse from equation. Identifying a hyperbola from an equation. Identifying circles and parabolas from equations. Hyperbola and parabola examples. Tangent Line Hyperbola Relationship (very optional). IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 1. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 2. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 3. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 4. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Common Tangent Part 5. IIT JEE Circle Hyperbola Intersection.
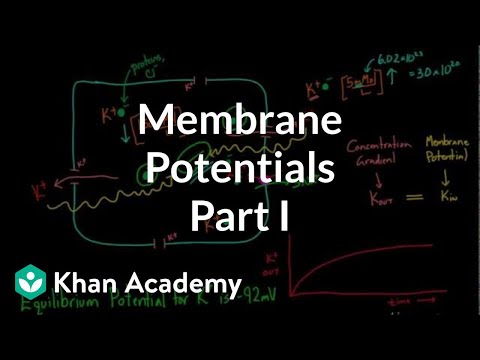
Check out the flow of positive charge through the heart that happens every time your heart beats! Learn how the heart is able to keep a regular rate and rhythm throughout your life. Membrane Potentials - Part 1. Membrane Potentials - Part 2. Permeability and Membrane Potentials. Action Potentials in Pacemaker Cells. Action Potentials in Cardiac Myocytes. Reseting Cardiac Concentration Gradients. Electrical System of the Heart. Depolarization Waves Flowing through the Heart. A Race to Keep Pace!. Thinking about Heartbeats. New Perspective on the Heart. Membrane Potentials - Part 1. Membrane Potentials - Part 2. Permeability and Membrane Potentials. Action Potentials in Pacemaker Cells. Action Potentials in Cardiac Myocytes. Reseting Cardiac Concentration Gradients. Electrical System of the Heart. Depolarization Waves Flowing through the Heart. A Race to Keep Pace!. Thinking about Heartbeats. New Perspective on the Heart.
Basic trigonometry. Example: Using soh cah toa. Trigonometry 0.5. Basic trigonometry II. Trigonometry 1. Secant (sec), cosecant (csc) and cotangent (cot) example. Example: Using trig to solve for missing information. Reciprocal trig functions. Trigonometry 1.5. Example: Calculator to evaluate a trig function. Example: Trig to solve the sides and angles of a right triangle. Trigonometry 2. Example: Solving a 30-60-90 triangle. Special right triangles. Using Trig Functions. Using Trig Functions Part II. Introduction to radians. Radian and degree conversion practice. Example: Radian measure and arc length. Example: Converting degrees to radians. Degrees to radians. Example: Converting radians to degrees. Radians to degrees. Radians and degrees. Radians and degrees. Unit circle definition of trig functions. Example: Unit circle definition of sin and cos. Example: Using the unit circle definition of trig functions. Example: Trig function values using unit circle definition. Example: The signs of sine and cosecant. Unit Circle Manipulative. Unit circle. Example: Graph, domain, and range of sine function. Example: Graph of cosine. Example: Intersection of sine and cosine. Example: Amplitude and period. Example: Amplitude and period transformations. Example: Amplitude and period cosine transformations. Example: Figure out the trig function. Graphs of sine and cosine. Graph of the sine function. Graphs of trig functions. Graphing trig functions. More trig graphs. Determining the equation of a trigonometric function. Inverse Trig Functions: Arcsin. Inverse Trig Functions: Arccos. Inverse Trig Functions: Arctan. Example: Calculator to evaluate inverse trig function. Inverse trig functions. Tau versus Pi. Pi Is (still) Wrong.. Basic trigonometry. Example: Using soh cah toa. Trigonometry 0.5. Basic trigonometry II. Trigonometry 1. Secant (sec), cosecant (csc) and cotangent (cot) example. Example: Using trig to solve for missing information. Reciprocal trig functions. Trigonometry 1.5. Example: Calculator to evaluate a trig function. Example: Trig to solve the sides and angles of a right triangle. Trigonometry 2. Example: Solving a 30-60-90 triangle. Special right triangles. Using Trig Functions. Using Trig Functions Part II. Introduction to radians. Radian and degree conversion practice. Example: Radian measure and arc length. Example: Converting degrees to radians. Degrees to radians. Example: Converting radians to degrees. Radians to degrees. Radians and degrees. Radians and degrees. Unit circle definition of trig functions. Example: Unit circle definition of sin and cos. Example: Using the unit circle definition of trig functions. Example: Trig function values using unit circle definition. Example: The signs of sine and cosecant. Unit Circle Manipulative. Unit circle. Example: Graph, domain, and range of sine function. Example: Graph of cosine. Example: Intersection of sine and cosine. Example: Amplitude and period. Example: Amplitude and period transformations. Example: Amplitude and period cosine transformations. Example: Figure out the trig function. Graphs of sine and cosine. Graph of the sine function. Graphs of trig functions. Graphing trig functions. More trig graphs. Determining the equation of a trigonometric function. Inverse Trig Functions: Arcsin. Inverse Trig Functions: Arccos. Inverse Trig Functions: Arctan. Example: Calculator to evaluate inverse trig function. Inverse trig functions. Tau versus Pi. Pi Is (still) Wrong..
You have probably been wondering whether our powers of algebraic problem solving break down if we divide by the variable or we have entire expressions in denominator of a fraction. Well, they don't! In this topic, you'll learn how to interpret and manipulate rational expressions (when you have one algebraic expression divided by another)!. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Simplifying Rational Expressions 1. Dividing polynomials by binomials 1. Simplifying Rational Expressions 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 2. Simplifying rational expressions 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions 3. Simplifying Rational Expressions Example 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 3. Simplifying rational expressions 3. Simplifying rational expressions 4. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 2. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 3. Subtracting Rational Expressions. Simplifying First for Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 0.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3. Multiplying and Simplifying Rational Expressions. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 4. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 5. Rationalizing Denominators of Expressions. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Partial Fraction Expansion 1. Partial Fraction Expansion 2. Partial Fraction Expansion 3. Partial fraction expansion. Ex 1 Multi step equation. Solving rational equations 1. Rational Equations. Solving Rational Equations 1. Solving Rational Equations 2. Solving Rational Equations 3. Applying Rational Equations 1. Applying Rational Equations 2. Applying Rational Equations 3. Solving rational equations 2. Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations. Extraneous solutions. Rational Inequalities. Rational Inequalities 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions Introduction. Simplifying Rational Expressions 1. Dividing polynomials by binomials 1. Simplifying Rational Expressions 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 2. Simplifying rational expressions 2. Simplifying Rational Expressions 3. Simplifying Rational Expressions Example 2. Dividing polynomials by binomials 3. Simplifying rational expressions 3. Simplifying rational expressions 4. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 2. Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions 3. Subtracting Rational Expressions. Simplifying First for Subtracting Rational Expressions. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 0.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 1.5. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 2. Adding and subtracting rational expressions 3. Multiplying and Simplifying Rational Expressions. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 1. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 2. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 1. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 2. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 3. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 4. Multiplying and dividing rational expressions 5. Rationalizing Denominators of Expressions. Asymptotes of Rational Functions. Another Rational Function Graph Example. A Third Example of Graphing a Rational Function. Partial Fraction Expansion 1. Partial Fraction Expansion 2. Partial Fraction Expansion 3. Partial fraction expansion. Ex 1 Multi step equation. Solving rational equations 1. Rational Equations. Solving Rational Equations 1. Solving Rational Equations 2. Solving Rational Equations 3. Applying Rational Equations 1. Applying Rational Equations 2. Applying Rational Equations 3. Solving rational equations 2. Extraneous Solutions to Rational Equations. Extraneous solutions. Rational Inequalities. Rational Inequalities 2.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.