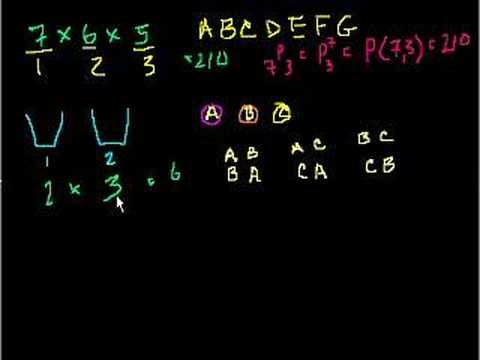Online courses directory (19947)
Quantitative Methods in Clinical and Public Health Research is the online adaptation of material from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health's classes in epidemiology and biostatistics. Principled investigations to monitor and thus improve the health of individuals are firmly based on a sound understanding of modern quantitative methods. This involves the ability to discover patterns and extract knowledge from health data on a sample of individuals and then to infer, with measured uncertainty, the unobserved population characteristics. This course will address this need by covering the principles of biostatistics and epidemiology used for public health and clinical research. These include outcomes measurement, measures of associations between outcomes and their determinants, study design options, bias and confounding, probability and diagnostic tests, confidence intervals and hypothesis testing, power and sample size determinations, life tables and survival methods, regression methods (both, linear and logistic), and sample survey techniques. Students will analyze sample data sets to acquire knowledge of appropriate computer software. By the end of the course the successful student should have attained a sound understanding of these methods and a solid foundation for further study.
FAQ
How much does it cost to take the course?
Nothing! The course is free.
When will assignments be due?
The course is organized into weeks, and each week will have its own set of assignments. Students will be expected to complete their homework each week.
Do I need any other materials to take the course?
Nope, as long as you’ve got a Mac or PC, you’ll be ready to take the course.
Will the course use any textbooks or software?
Yes! We'll have free access to the book "Principles of Biostatistics" written by Marcello Pagano (one of the Professors) and Kimberlee Gauvreau.
In addition to the textbook, we'll use Stata (a piece of software for doing statistical analysis).
Thanks to our friends at Statacorp, we'll have free copies of Stata available for all students to use for the duration of the course (Mac and PC only).
Do I need to watch the lectures live?
No. You can watch the lectures at your leisure.
Will certificates be awarded?
Yes. Online learners who achieve a passing grade in a course can earn a certificate of achievement. These certificates will indicate you have successfully completed the course, but will not include a specific grade. Certificates will be issued by edX under the name of either HarvardX, MITx or BerkeleyX, designating the institution from which the course originated. For the courses in Fall 2012, honor code certificates will be free.
HarvardX requires individuals who enroll in its courses on edX to abide by the terms of the edX honor code : https://www.edx.org/edx-terms-service. HarvardX will take appropriate corrective action in response to violations of the edX honor code, which may include dismissal from the HarvardX course; revocation of any certificates received for the HarvardX course; or other remedies as circumstances warrant. No refunds will be issued in the case of corrective action for such violations. Enrollees who are taking HarvardX courses as part of another program will also be governed by the academic policies of those programs.
HarvardX pursues the science of learning. By registering as an online learner in an HX course, you will also participate in research about learning. Read our research statement : http://harvardx.harvard.edu/research-statement to learn more.
Harvard University and HarvardX are committed to maintaining a safe and healthy educational and work environment in which no member of the community is excluded from participation in, denied the benefits of, or subjected to discrimination or harassment in our program. All members of the HarvardX community are expected to abide by Harvard policies on nondiscrimination, including sexual harassment, and the edX Terms of Service. If you have any questions or concerns, please contact harvardx@harvard.edu and/or report your experience through the edX contact form : https://www.edx.org/contact-us.
Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Expressing ratios as fractions. Describing ratios exercise. Describing ratios. Ratio word problem exercise example 1. Ratio word problem exercise example 2. Ratio word problems. Proportion validity example. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 2. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 3. Solving ratio problems with tables. Usain Bolt's Average Speed. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Rate problems 0.5. Multiple rates word problem. Rate problems 2. Converting pounds to ounces. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting Yards into Inches. Performing arithmetic calculations on units of volume. Application problems involving units of weight. Solving application problems involving units of volume. Gas cost for a roadtrip. Squirrel survival. Converting units of length. Unit Conversion Example: Drug Dosage. Unit Conversion with Fractions. Units. Speed translation. Unit conversion within the metric system. Converting within the metric system. Perimeter and Unit Conversion. Applying the Metric System. Conversion between metric units. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales. Introduction to Ratios (new HD version). Ratios as Fractions in Simplest Form. Simplifying Rates and Ratios. Expressing ratios as fractions. Describing ratios exercise. Describing ratios. Ratio word problem exercise example 1. Ratio word problem exercise example 2. Ratio word problems. Proportion validity example. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 2. Solving ratio problems with tables exercise 3. Solving ratio problems with tables. Usain Bolt's Average Speed. Finding Unit Rates. Finding Unit Prices. Rate problems 0.5. Multiple rates word problem. Rate problems 2. Converting pounds to ounces. Converting Gallons to quarts pints and cups. Converting Yards into Inches. Performing arithmetic calculations on units of volume. Application problems involving units of weight. Solving application problems involving units of volume. Gas cost for a roadtrip. Squirrel survival. Converting units of length. Unit Conversion Example: Drug Dosage. Unit Conversion with Fractions. Units. Speed translation. Unit conversion within the metric system. Converting within the metric system. Perimeter and Unit Conversion. Applying the Metric System. Conversion between metric units. U.S. Customary and Metric units. Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius. Comparing Celsius and Farenheit temperature scales.
chirality, stereoisomers, assigning absolute configuration using the R,S system, optical activity, diastereomers, meso compounds, fischer projections. Introduction to Chirality. Chiral Examples 1. Chiral Examples 2. Cahn-Ingold-Prelog System for Naming Enantiomers. R,S (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Naming System Example 2. chirality centers and stereoisomers. R,S system for determining absolute configuration. R,S system for cyclic compounds. optical activity I: theory. optical activity II: calculations. Stereoisomers, Enantiomers, Diastereomers, Constitutional Isomers and Meso Compounds. diastereomers. meso compounds. fischer projections. Introduction to Chirality. Chiral Examples 1. Chiral Examples 2. Cahn-Ingold-Prelog System for Naming Enantiomers. R,S (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Naming System Example 2. chirality centers and stereoisomers. R,S system for determining absolute configuration. R,S system for cyclic compounds. optical activity I: theory. optical activity II: calculations. Stereoisomers, Enantiomers, Diastereomers, Constitutional Isomers and Meso Compounds. diastereomers. meso compounds. fischer projections.
conjugation, conjugated dienes, addition reactions of conjugated dienes, diels-alder reaction, MO theory, color. addition reaction of conjugated dienes I: mechanism. addition reaction of conjugated dienes II: example. addition reaction of conjugated dienes III: control. diels-alder I: mechanism. diels-alder II: endo vs exo. diels-alder III: stereochemistry of dienophile. diels-alder IV: stereochemistry of diene. diels-alder V: regiochemistry. diels-alder VI: more regiochemistry. diels-alder VII: intramolecular. intro to molecular orbital (MO) theory. MO theory for butadiene. MO theory for Diels-Alder. intro to color theory. conjugation and color. color in organic molecules. addition reaction of conjugated dienes I: mechanism. addition reaction of conjugated dienes II: example. addition reaction of conjugated dienes III: control. diels-alder I: mechanism. diels-alder II: endo vs exo. diels-alder III: stereochemistry of dienophile. diels-alder IV: stereochemistry of diene. diels-alder V: regiochemistry. diels-alder VI: more regiochemistry. diels-alder VII: intramolecular. intro to molecular orbital (MO) theory. MO theory for butadiene. MO theory for Diels-Alder. intro to color theory. conjugation and color. color in organic molecules.
Demand Curve as Marginal Benefit Curve. Consumer Surplus Introduction. Total Consumer Surplus as Area. Producer Surplus. Rent Control and Deadweight Loss. Minimum Wage and Price Floors. Taxation and Dead Weight Loss. Percentage Tax on Hamburgers. Taxes and Perfectly Inelastic Demand. Taxes and Perfectly Elastic Demand. Negative Externalities. Taxes for Factoring in Negative Externalities. Positive Externalities. Tragedy of the Commons. Demand Curve as Marginal Benefit Curve. Consumer Surplus Introduction. Total Consumer Surplus as Area. Producer Surplus. Rent Control and Deadweight Loss. Minimum Wage and Price Floors. Taxation and Dead Weight Loss. Percentage Tax on Hamburgers. Taxes and Perfectly Inelastic Demand. Taxes and Perfectly Elastic Demand. Negative Externalities. Taxes for Factoring in Negative Externalities. Positive Externalities. Tragedy of the Commons.
Trigonometry Identity Review/Fun. Trigonometric Identities. Examples using Pythagorean identities to simplify trigonometric expressions. Pythagorean identities. Proof: sin(a+b) = (cos a)(sin b) + (sin a)(cos b). Proof: cos(a+b) = (cos a)(cos b)-(sin a)(sin b). Trig identities part 2 (part 4 if you watch the proofs). Trig identies part 3 (part 5 if you watch the proofs). Cosine addition identity example. Double angle formula for cosine example. Addition and subtraction trig identities. Navigation Word Problem. Fun Trig Problem. IIT JEE Trigonometry Problem 1. IIT JEE Trigonometric Maximum. IIT JEE Trigonometric Constraints. Trigonometric System Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. Trigonometry word problems (part 1). Trigonometry word problems (part 2). Ferris Wheel Trig Problem. Ferris Wheel Trig Problem (part 2). Law of cosines example. Proof of the law of cosines. Law of cosines. Proof: Law of Sines. Trigonometry Identity Review/Fun. Trigonometric Identities. Examples using Pythagorean identities to simplify trigonometric expressions. Pythagorean identities. Proof: sin(a+b) = (cos a)(sin b) + (sin a)(cos b). Proof: cos(a+b) = (cos a)(cos b)-(sin a)(sin b). Trig identities part 2 (part 4 if you watch the proofs). Trig identies part 3 (part 5 if you watch the proofs). Cosine addition identity example. Double angle formula for cosine example. Addition and subtraction trig identities. Navigation Word Problem. Fun Trig Problem. IIT JEE Trigonometry Problem 1. IIT JEE Trigonometric Maximum. IIT JEE Trigonometric Constraints. Trigonometric System Example. 2003 AIME II Problem 11. 2003 AIME II Problem 14. Trigonometry word problems (part 1). Trigonometry word problems (part 2). Ferris Wheel Trig Problem. Ferris Wheel Trig Problem (part 2). Law of cosines example. Proof of the law of cosines. Law of cosines. Proof: Law of Sines.
Permutations and combinations. Using combinatorics to solve questions in probability. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations. Permutations. Combinations. Counting 2. Example: Ways to arrange colors. Example: 9 card hands. Example: Ways to pick officers. Permutations. Combinations. Permutations and combinations. Example: Probability through counting outcomes. Example: All the ways you can flip a coin. Getting Exactly Two Heads (Combinatorics). Probability and Combinations (part 2). Probability using Combinations. Exactly Three Heads in Five Flips. Example: Different ways to pick officers. Example: Combinatorics and probability. Example: Lottery probability. Mega Millions Jackpot Probability. Generalizing with Binomial Coefficients (bit advanced). Conditional Probability and Combinations. Conditional Probability (Bayes Theorem) Visualized. Birthday Probability Problem. Probability with permutations and combinations.
Measures of central tendency and dispersion. Mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance. Statistics intro: mean, median and mode. Example: Finding mean, median and mode. Mean median and mode. Exploring Mean and Median Module. Exploring mean and median. Average word problems. Sample mean versus population mean.. Reading Box-and-Whisker Plots. Constructing a box-and-whisker plot. Box-and-Whisker Plots. Creating box and whisker plots. Example: Range and mid-range. Range, Variance and Standard Deviation as Measures of Dispersion. Variance of a population. Sample variance. Review and intuition why we divide by n-1 for the unbiased sample variance. Simulation showing bias in sample variance. Unbiased Estimate of Population Variance. Another simulation giving evidence that (n-1) gives us an unbiased estimate of variance. Simulation providing evidence that (n-1) gives us unbiased estimate. Will it converge towards -1?. Variance. Population standard deviation. Sample standard deviation and bias. Statistics: Standard Deviation. Exploring Standard Deviation 1 Module. Exploring standard deviation 1. Standard deviation. Statistics: Alternate Variance Formulas. Statistics: The Average. Statistics: Variance of a Population. Statistics: Sample Variance.
This tutorial is the meat of much of classical physics. We think about what a force is and how Newton changed the world's (and possibly your) view of how reality works. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion Concepts. Newton's First Law of Motion. Newton's First Law. Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's Third Law of Motion. All of Newton's Laws of Motion. Normal Force and Contact Force. Normal Force in an Elevator. Balanced and Unbalanced Forces. Unbalanced Forces and Motion. Slow Sock on Lubricon VI. Normal Forces on Lubricon VI. Inclined Plane Force Components. Ice Accelerating Down an Incline. Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Correction to Force of Friction Keeping the Block Stationary. Force of Friction Keeping Velocity Constant. Intuition on Static and Kinetic Friction Comparisons. Static and Kinetic Friction Example. Introduction to Tension. Introduction to Tension (Part 2). Tension in an accelerating system and pie in the face.
Topics covered in a traditional college level introductory macroeconomics course. Introduction to Economics. Circular Flow of Income and Expenditures. Parsing Gross Domestic Product. More on Final and Intermediate GDP Contributions. Investment and Consumption. Income and Expenditure Views of GDP. Components of GDP. Examples of Accounting for GDP. Real GDP and Nominal GDP. GDP Deflator. Example Calculating Real GDP with a Deflator. Introduction to Inflation. Actual CPI-U Basket of Goods. Inflation Data. Moderate Inflation in a Good Economy. Stagflation. Real and Nominal Return. Calculating Real Return in Last Year Dollars. Relation Between Nominal and Real Returns and Inflation. Deflation. Velocity of Money Rather than Quantity Driving Prices. Deflation Despite Increases in Money Supply. Deflationary Spiral. Hyperinflation. Unemployment Rate Primer. Phillips Curve. Interest as Rent for Money. Money Supply and Demand Impacting Interest Rates. The Business Cycle. Aggregate Demand. Shifts in Aggregate Demand. Long-Run Aggregate Supply. Short Run Aggregate Supply. Demand-Pull Inflation under Johnson. Real GDP driving Price. Cost Push Inflation. Monetary and Fiscal Policy. Tax Lever of Fiscal Policy. Breakdown of Gas Prices. Short-Run Oil Prices. Keynesian Economics. Risks of Keynesian Thinking. Overview of Fractional Reserve Banking. Weaknesses of Fractional Reserve Lending. Full Reserve Banking. Money Supply- M0 M1 and M2. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting part 1. Simple Fractional Reserve Accounting (part 2). MPC and Multiplier. Mathy Version of MPC and Multiplier (optional). Consumption Function Basics. Generalized Linear Consumption Function. Consumption Function with Income Dependent Taxes. Keynesian Cross. Details on Shifting Aggregate Planned Expenditures. Keynesian Cross and the Multiplier. Investment and Real Interest Rates. Connecting the Keynesian Cross to the IS-Curve. Loanable Funds Interpretation of IS Curve. LM part of the IS-LM model. Government Spending and the IS-LM model. Balance of Payments- Current Account. Balance of Payments- Capital Account. Why Current and Capital Accounts Net Out. Accumulating Foreign Currency Reserves. Using Reserves to Stabilize Currency. Speculative Attack on a Currency. Financial Crisis in Thailand Caused by Speculative Attack. Math Mechanics of Thai Banking Crisis.
American Call Options. Basic Shorting. American Put Options. Call Option as Leverage. Put vs. Short and Leverage. Call Payoff Diagram. Put Payoff Diagram. Put as Insurance. Put-Call Parity. Long Straddle. Put Writer Payoff Diagrams. Call Writer Payoff Diagram. Arbitrage Basics. Put-Call Parity Arbitrage I. Put-Call Parity Arbitrage II. Put-Call Parity Clarification. Actual Option Quotes. Option Expiration and Price. Forward Contract Introduction. Futures Introduction. Motivation for the Futures Exchange. Futures Margin Mechanics. Verifying Hedge with Futures Margin Mechanics. Futures and Forward Curves. Contango from Trader Perspective. Severe Contango Generally Bearish. Backwardation Bullish or Bearish. Futures Curves II. Contango. Backwardation. Contango and Backwardation Review. Upper Bound on Forward Settlement Price. Lower Bound on Forward Settlement Price. Arbitraging Futures Contract. Arbitraging Futures Contracts II. Futures Fair Value in the Pre-Market. Interpreting Futures Fair Value in the PreMarket. Mortgage Back Security Overview. Mortgage-Backed Securities I. Mortgage-backed securities II. Mortgage-backed securities III. Collateralized Debt Obligation Overview. Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO). Credit Default Swaps (CDS) Intro. Credit Default Swaps. Credit Default Swaps 2. Use Cases for Credit Default Swaps. Financial Weapons of Mass Destruction. Interest Rate Swap 1. Interest Rate Swap 2. Introduction to the Black Scholes Formula. Implied volatility. American Call Options. Basic Shorting. American Put Options. Call Option as Leverage. Put vs. Short and Leverage. Call Payoff Diagram. Put Payoff Diagram. Put as Insurance. Put-Call Parity. Long Straddle. Put Writer Payoff Diagrams. Call Writer Payoff Diagram. Arbitrage Basics. Put-Call Parity Arbitrage I. Put-Call Parity Arbitrage II. Put-Call Parity Clarification. Actual Option Quotes. Option Expiration and Price. Forward Contract Introduction. Futures Introduction. Motivation for the Futures Exchange. Futures Margin Mechanics. Verifying Hedge with Futures Margin Mechanics. Futures and Forward Curves. Contango from Trader Perspective. Severe Contango Generally Bearish. Backwardation Bullish or Bearish. Futures Curves II. Contango. Backwardation. Contango and Backwardation Review. Upper Bound on Forward Settlement Price. Lower Bound on Forward Settlement Price. Arbitraging Futures Contract. Arbitraging Futures Contracts II. Futures Fair Value in the Pre-Market. Interpreting Futures Fair Value in the PreMarket. Mortgage Back Security Overview. Mortgage-Backed Securities I. Mortgage-backed securities II. Mortgage-backed securities III. Collateralized Debt Obligation Overview. Collateralized Debt Obligation (CDO). Credit Default Swaps (CDS) Intro. Credit Default Swaps. Credit Default Swaps 2. Use Cases for Credit Default Swaps. Financial Weapons of Mass Destruction. Interest Rate Swap 1. Interest Rate Swap 2. Introduction to the Black Scholes Formula. Implied volatility.
How do you decide what to produce or trade? How can you maximize happiness in a world of scarcity. What are you giving up when you choose something (i.e., opportunity cost)?. Production Possibilities Frontier. Opportunity Cost. Increasing Opportunity Cost. Allocative Efficiency and Marginal Benefit. Economic Growth through Investment. Comparative Advantage Specialization and Gains from Trade. Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage. Marginal Utility. Equalizing Marginal Utility per Dollar Spent. Deriving Demand Curve from Tweaking Marginal Utility per Dollar. Budget Line. Indifference Curves and Marginal Rate of Substitution. Optimal Point on Budget Line. Types of Indifference Curves. Production Possibilities Frontier. Opportunity Cost. Increasing Opportunity Cost. Allocative Efficiency and Marginal Benefit. Economic Growth through Investment. Comparative Advantage Specialization and Gains from Trade. Comparative Advantage and Absolute Advantage. Marginal Utility. Equalizing Marginal Utility per Dollar Spent. Deriving Demand Curve from Tweaking Marginal Utility per Dollar. Budget Line. Indifference Curves and Marginal Rate of Substitution. Optimal Point on Budget Line. Types of Indifference Curves.
nomenclature and reactions of amines. Amine Naming Introduction. Amine Naming 2. Amine as Nucleophile in Sn2 Reaction. Amine in Sn2 part 2. Sn1 Amine Reaction. Amine Naming Introduction. Amine Naming 2. Amine as Nucleophile in Sn2 Reaction. Amine in Sn2 part 2. Sn1 Amine Reaction.
Economic profit vs. accounting profit. Average total cost (ATC) and marginal cost (MC). Marginal product of labor (MPL). Price discrimination. Economic Profit vs Accounting Profit. Depreciation and Opportunity Cost of Capital. Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. Marginal Revenue Below Average Total Cost. Long Term Supply Curve and Economic Profit. Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost.. Visualizing Average Costs and Marginal Costs as Slope. A Firm's Marginal Product Revenue Curve. How Many People to Hire Given the MPR curve. Adding Demand Curves. First Degree Price Discrimination. Economic Profit vs Accounting Profit. Depreciation and Opportunity Cost of Capital. Marginal Cost and Average Total Cost. Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost. Marginal Revenue Below Average Total Cost. Long Term Supply Curve and Economic Profit. Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost.. Visualizing Average Costs and Marginal Costs as Slope. A Firm's Marginal Product Revenue Curve. How Many People to Hire Given the MPR curve. Adding Demand Curves. First Degree Price Discrimination.
Making inferences based on sample data. Confidence intervals. Margin of error. Hypothesis testing. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic. Introduction to the Normal Distribution. Normal Distribution Excel Exercise. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Qualitative sense of normal distributions. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: Empirical Rule. ck12.org Normal Distribution Problems: z-score. ck12.org Exercise: Standard Normal Distribution and the Empirical Rule. Empirical rule. ck12.org: More Empirical Rule and Z-score practice. Z scores 1. Z scores 2. Z scores 3. Central Limit Theorem. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean. Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean 2. Standard Error of the Mean. Sampling Distribution Example Problem. Confidence Interval 1. Confidence Interval Example. Small Sample Size Confidence Intervals. Mean and Variance of Bernoulli Distribution Example. Bernoulli Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas. Margin of Error 1. Margin of Error 2. Hypothesis Testing and P-values. One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests. Type 1 Errors. Z-statistics vs. T-statistics. Small Sample Hypothesis Test. T-Statistic Confidence Interval. Large Sample Proportion Hypothesis Testing. Variance of Differences of Random Variables. Difference of Sample Means Distribution. Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Clarification of Confidence Interval of Difference of Means. Hypothesis Test for Difference of Means. Comparing Population Proportions 1. Comparing Population Proportions 2. Hypothesis Test Comparing Population Proportions. Chi-Square Distribution Introduction. Pearson's Chi Square Test (Goodness of Fit). Contingency Table Chi-Square Test. ANOVA 1 - Calculating SST (Total Sum of Squares). ANOVA 2 - Calculating SSW and SSB (Total Sum of Squares Within and Between).avi. ANOVA 3 -Hypothesis Test with F-Statistic.
You understand velocity and acceleration well in one-dimension. Now we can explore scenarios that are even more fun. With a little bit of trigonometry (you might want to review your basic trig, especially what sin and cos are), we can think about whether a baseball can clear the "green monster" at Fenway Park. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2. Visualizing Vectors in 2 Dimensions. Projectile at an Angle. Different Way to Determine Time in Air. Launching and Landing on Different Elevations. Total Displacement for Projectile. Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Correction to Total Final Velocity for Projectile. Projectile on an Incline. Unit Vectors and Engineering Notation. Clearing the Green Monster at Fenway. Green Monster at Fenway Part 2. Unit Vector Notation. Unit Vector Notation (part 2). Projectile Motion with Ordered Set Notation. Optimal angle for a projectile part 1. Optimal angle for a projectile part 2 - Hangtime. Optimal angle for a projectile part 3 - Horizontal distance as a function of angle (and speed). Optimal angle for a projectile part 4 Finding the optimal angle and distance with a bit of calculus. Race Cars with Constant Speed Around Curve. Centripetal Force and Acceleration Intuition. Visual Understanding of Centripetal Acceleration Formula. Calculus proof of centripetal acceleration formula. Loop De Loop Question. Loop De Loop Answer part 1. Loop De Loop Answer part 2.
Overview of the videos, exercises, reports, and Computer Science resources available on Khan Academy, with emphasis on how resources can be used in classrooms. For more information, check out http://www.khanacademy.org/toolkit/ka-resources. For a mapping of Khan Academy content to Common Core standards, check out khanacademy.org/commoncore. Khan Academy overview. Khan Academy reports overview. Khan Academy Exercise Overview. Khan Academy Computer Science in the classroom. Khan Academy overview. Khan Academy reports overview. Khan Academy Exercise Overview. Khan Academy Computer Science in the classroom.
Understanding how we can map one set of vectors to another set. Matrices used to define linear transformations. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible. A more formal understanding of functions. Vector Transformations. Linear Transformations. Matrix Vector Products as Linear Transformations. Linear Transformations as Matrix Vector Products. Image of a subset under a transformation. im(T): Image of a Transformation. Preimage of a set. Preimage and Kernel Example. Sums and Scalar Multiples of Linear Transformations. More on Matrix Addition and Scalar Multiplication. Linear Transformation Examples: Scaling and Reflections. Linear Transformation Examples: Rotations in R2. Rotation in R3 around the X-axis. Unit Vectors. Introduction to Projections. Expressing a Projection on to a line as a Matrix Vector prod. Compositions of Linear Transformations 1. Compositions of Linear Transformations 2. Matrix Product Examples. Matrix Product Associativity. Distributive Property of Matrix Products. Introduction to the inverse of a function. Proof: Invertibility implies a unique solution to f(x)=y. Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions. Relating invertibility to being onto and one-to-one. Determining whether a transformation is onto. Exploring the solution set of Ax=b. Matrix condition for one-to-one trans. Simplifying conditions for invertibility. Showing that Inverses are Linear. Deriving a method for determining inverses. Example of Finding Matrix Inverse. Formula for 2x2 inverse. 3x3 Determinant. nxn Determinant. Determinants along other rows/cols. Rule of Sarrus of Determinants. Determinant when row multiplied by scalar. (correction) scalar multiplication of row. Determinant when row is added. Duplicate Row Determinant. Determinant after row operations. Upper Triangular Determinant. Simpler 4x4 determinant. Determinant and area of a parallelogram. Determinant as Scaling Factor. Transpose of a Matrix. Determinant of Transpose. Transpose of a Matrix Product. Transposes of sums and inverses. Transpose of a Vector. Rowspace and Left Nullspace. Visualizations of Left Nullspace and Rowspace. Rank(A) = Rank(transpose of A). Showing that A-transpose x A is invertible.
We explore creating and moving between various coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems. Orthogonal Complements. dim(V) + dim(orthogonal complement of V)=n. Representing vectors in Rn using subspace members. Orthogonal Complement of the Orthogonal Complement. Orthogonal Complement of the Nullspace. Unique rowspace solution to Ax=b. Rowspace Solution to Ax=b example. Projections onto Subspaces. Visualizing a projection onto a plane. A Projection onto a Subspace is a Linear Transforma. Subspace Projection Matrix Example. Another Example of a Projection Matrix. Projection is closest vector in subspace. Least Squares Approximation. Least Squares Examples. Another Least Squares Example. Coordinates with Respect to a Basis. Change of Basis Matrix. Invertible Change of Basis Matrix. Transformation Matrix with Respect to a Basis. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example. Alternate Basis Transformation Matrix Example Part 2. Changing coordinate systems to help find a transformation matrix. Introduction to Orthonormal Bases. Coordinates with respect to orthonormal bases. Projections onto subspaces with orthonormal bases. Finding projection onto subspace with orthonormal basis example. Example using orthogonal change-of-basis matrix to find transformation matrix. Orthogonal matrices preserve angles and lengths. The Gram-Schmidt Process. Gram-Schmidt Process Example. Gram-Schmidt example with 3 basis vectors. Introduction to Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors. Proof of formula for determining Eigenvalues. Example solving for the eigenvalues of a 2x2 matrix. Finding Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces example. Eigenvalues of a 3x3 matrix. Eigenvectors and Eigenspaces for a 3x3 matrix. Showing that an eigenbasis makes for good coordinate systems.
Cash Accounting. Accrual Basis of Accounting. Comparing Accrual and Cash Accounting. Balance Sheet and Income Statement Relationship. Basic Cash Flow Statement. Doing the example with Accounts Payable growing. Fair Value Accounting. Expensing a Truck leads to inconsistent performance. Depreciating the truck. Depreciation in Cash Flow. Amortization and Depreciation. Cash Accounting. Accrual Basis of Accounting. Comparing Accrual and Cash Accounting. Balance Sheet and Income Statement Relationship. Basic Cash Flow Statement. Doing the example with Accounts Payable growing. Fair Value Accounting. Expensing a Truck leads to inconsistent performance. Depreciating the truck. Depreciation in Cash Flow. Amortization and Depreciation.
Trusted paper writing service WriteMyPaper.Today will write the papers of any difficulty.